Today topic: How to Turn an Android Phone into a Hacking Device Without Root
We’ll start by installing an SSH client, which will be the primary app for interacting with the Debian OS. Then, I’ll walk through some OS setup tips and importing the Kali Linux repository to really turn Android into a hacking device. As some readers may know, Kali Linux is based on the Debian operating system, so importing their repository won’t cause anything to break or become unreliable.
Step 1. Install the ConnectBot App (Optional)
UserLAnd recently added a built-in SSH functionality, so this step is no longer required. However, third-party SSH clients can still be used if preferred.
ConnectBot is an open source SSH client designed for Android smartphones, which allows you to securely connect with SSH servers. This will be the primary way of interacting with the new UserLAnd Debian operating system. If you don’t use or have access to Google Play, ConnectBot.
Step 2. Install the UserLAnd App
I’ve already covered what UserLAnd is and does above, so I won’t go over anything else in detail here. The important thing is that you install it, and you can do so using either Google Play.
Step 3. Create a New Filesystem
When the installation is complete, open UserLAnd, and view the “Apps” tab. Refresh the tab and wait a few minutes for the distributions to populate.
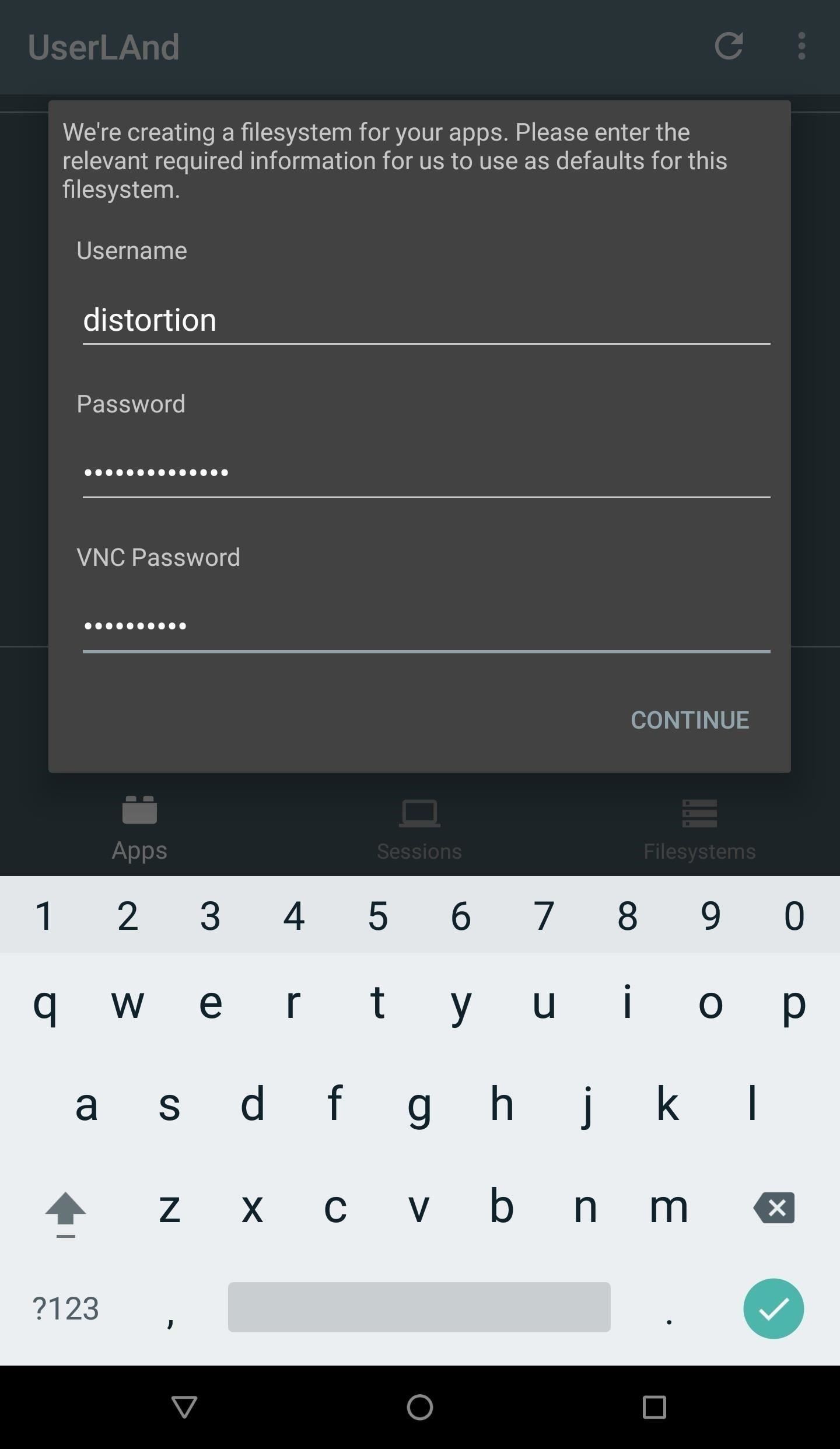
The Kali Linux OS has recently been added to the list of available distributions. Select “Kali” or “Debian” and the UserLAnd app will prompt for credentials. Create a username, password, and VNC password. The “Password” will allow access to the SSH server started when the filesystem is finished installing. The “VNC Password” won’t be used in this tutorial but is required to proceed with the installation.
UserLAnd will then download the necessary executables and scripts from its GitHub repository that are used to create the filesystems. The time it takes to download and extract the required assets will vary based on the Android CPU and internet connection speed. The installation process took up to 20 minutes to complete in some tests, so be patient.
Step 4. Interact with the Filesystem
When the installation is complete, head over to the “Sessions” tab, and select the newly created option. UserLAnd will automatically attempt to open ConnectBot and ask “Are you sure you want to continue connecting?” Tap “Yes,” and enter the password created in the previous step.
At this point, syncing a Bluetooth keyboard to the phone will make setting up the OS easier, but isn’t required. If you don’t use a Bluetooth keyboard, I recommend installing Hacker’s Keyboard from the Play Store, and you’ll see why as we continue.
Step 5. Update the OS
The first thing to do after installing a new operating system on your Android phone is making sure the system is fully up to date. This can be done by first using su to create a root shell. Next, use the apt-get update && apt-get dist-upgrade command.
distortion@localhost:~$ su
root@localhost: /home/distortion# apt-get update && apt-get dist-upgrade
Ign:1 http://cdn-fastly.deb.debian.org/debian stable InRelease
Get:2 http://cdn-fastly.deb.debian.org/debian stable-updates InRelease [91.0 kB]
Hit:3 http://cdn-fastly.deb.debian.org/debian stable Release
Get:4 http://cdn-fastly.deb.debian.org/debian stable Release.gpg [2434 B]
Get:5 http://cdn-fastly.deb.debian.org/debian stable-updates/main arm64 Packages [5096 B]
Get:6 http://cdn-fastly.deb.debian.org/debian stable-updates/main Translation-en [4512 B]
Get:7 http://cdn-fastly.deb.debian.org/debian stable/main Translation-en [5393 B]
Get:8 http://cdn-fastly.deb.debian.org/debian stable/contrib arm64 Packages [29.9 kB]
Get:9 http://cdn-fastly.deb.debian.org/debian stable/contrib Translation-en [45.9 kB]
Get:10 http://cdn-fastly.deb.debian.org/debian stable/non-free arm64 Package [50.8 kB]
Get:11 http://cdn-fastly.deb.debian.org/debian stablenon-free Translation-en [80.6 kB]
Fetched 5714 kB in 31s (183 kB/s)
Reading package lists... Done
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Calculating upgrade... Done
The following packages will be upgraded:
tzdata
1 upgraded, 0 newly intalled, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded.
Need to get 270 kB of archives.
After this operation, 1024 B of additional disk space will be used.
Do you want to continue? [Y/n]In the case of the above output, there’s only one package that needed updating, but this might not always be true.
Step 6. Install Essential Software
This new filesystem is extremely barebones and doesn’t include very much software by default. Below are a few packages recommended for everyday Debian and Kali users. Some packages aren’t required but will make it easier to follow along in future articles where Android is used as the primary hacking device.
- screen — Screen is a terminal multiplexer that allows users to run and alternate between several terminal sessions simultaneously. This is one of the most vital packages to install when using UserLAnd. Android phones don’t handle prolonged SSH sessions well and tend to break connections for no apparent reason. Such breakage can cause running commands to fail with no way of reconnecting to the session to view the progress. Use Screen to maintain persistent shell sessions.
- net-tools — Net-tools is a suite of tools containing ifconfig, netstat, route, and several other useful networking applications.
- netcat — Netcat is a feature-rich UNIX utility designed to be a reliable tool for creating TCP and UDP connections. Netcat can be used to create and interact with simple macOS backdoors.
- neofetch — Neofetch (shown in the cover photo of this article) is a cross-platform system information gathering tool. It conveniently displays system specifications alongside the distribution logo. There’s no real function for this package other than showing-off the distribution to coworkers and friends or creating cover photos for WonderHowTo. Neofetch is a little buggy with UserLAnd distros, but you may want to know how I created the cover photo, so I’m including it here.
- gnupg — GnuPG (sometimes referred to as gpg) is generally used for encrypting files and securing email communications. Some installer scripts (like Metasploit) use gpg in order to import their software signing keys. It’s possible to manually install Metasploit without gpg, but it will make the process less complicated.
Step 7. Import the Kali Linux Repository (Conditional)
If you installed the Kali OS in Step 3, this step can be skipped. For Debian OS users, importing the Kali repository into your distribution isn’t mandatory. However, doing so will allow for quick installations of applications such as sqlmap, Commix, Bettercap, Nikto, dnsmap, and hundreds of packages that can’t be found in Debian’s default repositories.
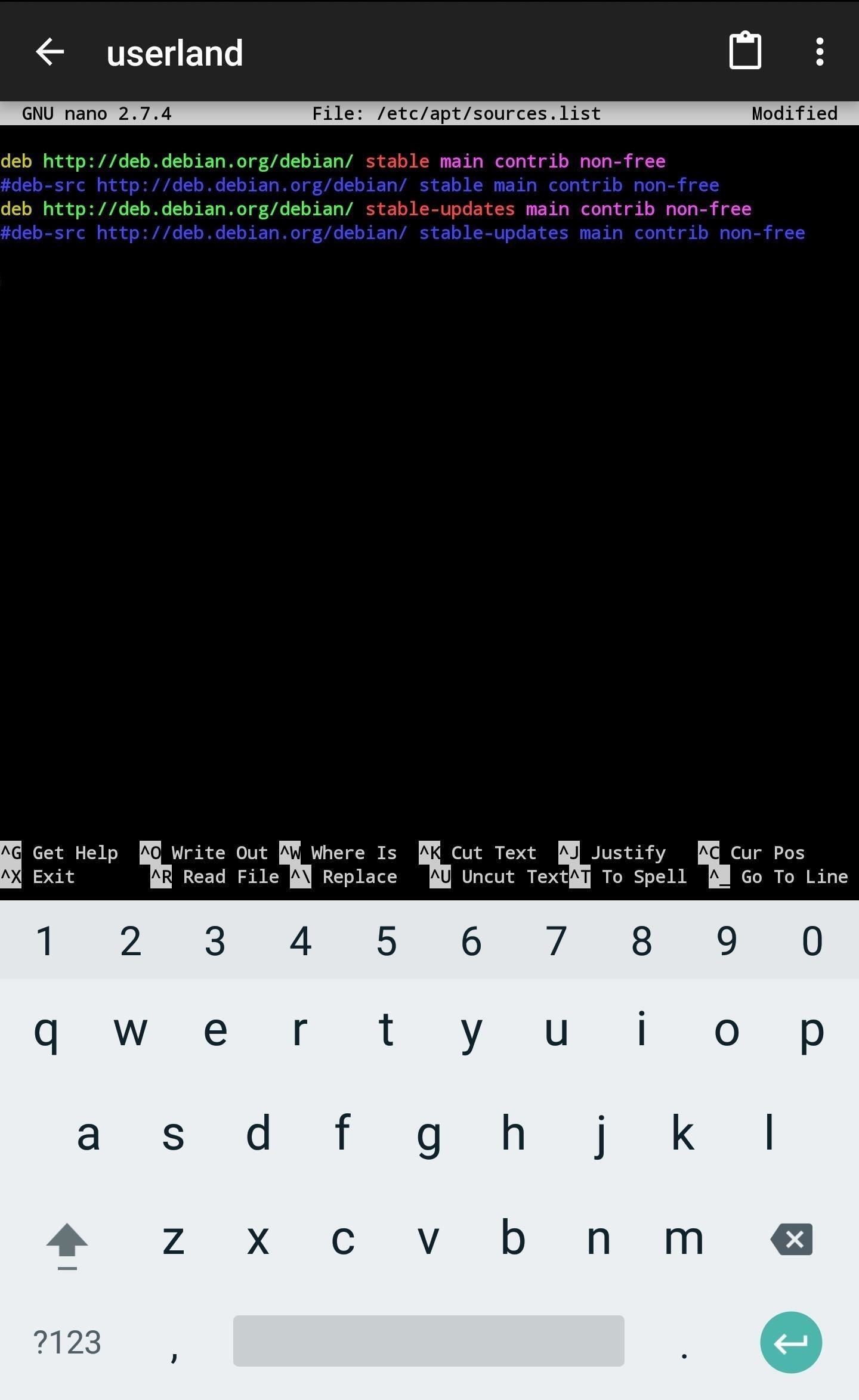
To start importing the Kali Linux repository, use nano to add Kali’s repository to the /etc/apt/sources.list file.
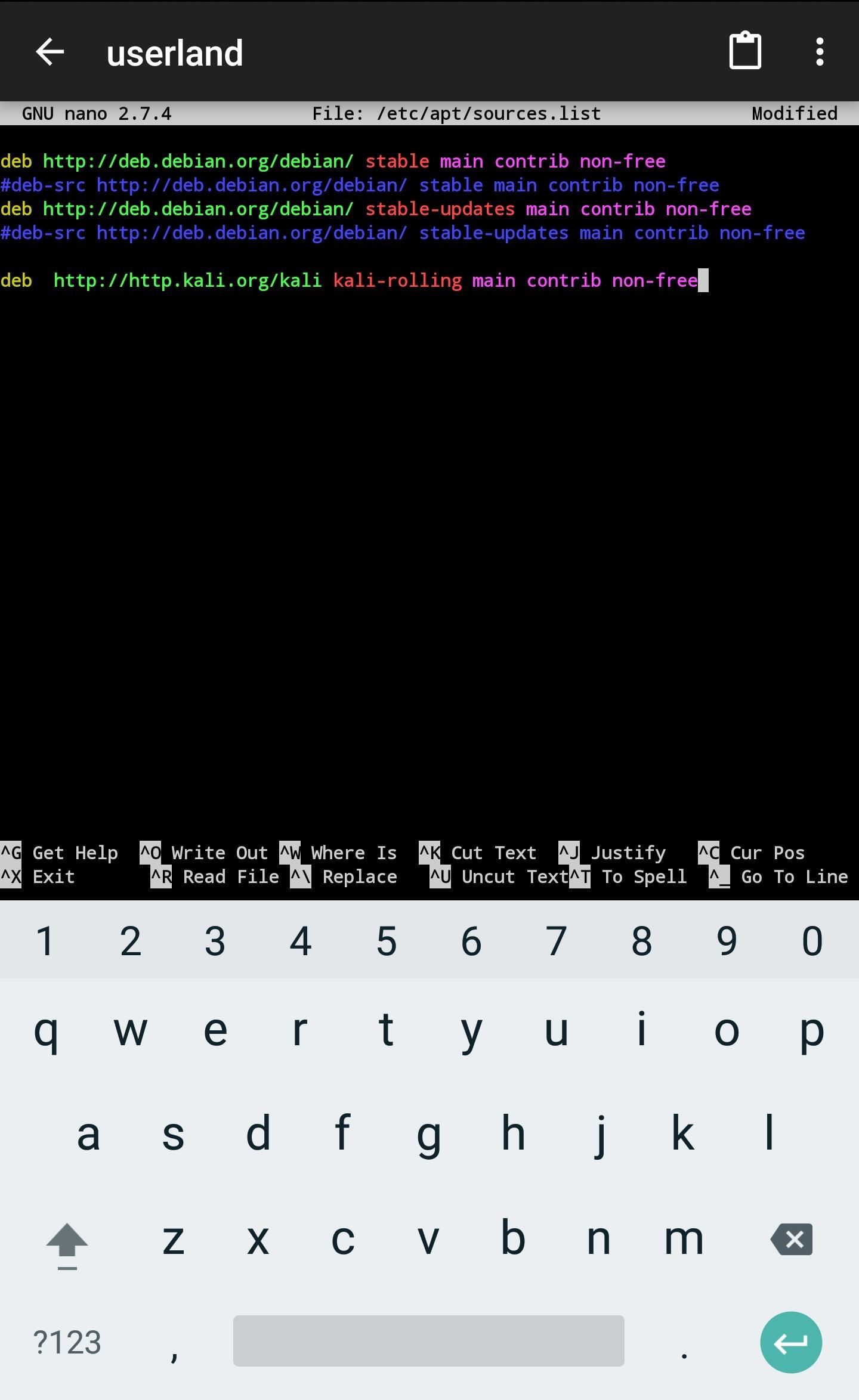
nano /etc/apt/sources.listAdd the below line to the bottom of the file (shown below), then use Ctrl + X to exit and save the changes. ConnectBot has on-screen buttons for keys like Ctrl and Shift. Alternatively, a Bluetooth keyboard or the Hacker’s Keyboard app will come in handy for exiting the nano terminal.
deb http://http.kali.org/kali kali-rolling main contrib non-freeThen, add the Kali signing key using the following wget command.
wget -q -O - https://www.kali.org/archive-key.asc | apt-key add -
If the command was successful, the terminal will return “OK” (shown below). Finally, update the APT cache using the apt-get update command.
root@localhost:/home/distortion# wget -q -O - https://www.kali.org/archive-key.asc | apt-key add -
OK
root@localhost:/home/distortion# apt-get update
Ign:1 http://cdn-fastly.deb.debian.org/debian stable InRelease
Hit:3 http://cdn-fastly.deb.debian.org/debian stable-updates InRelease
Hit:4 http://cdn-fastly.deb.debian.org/debian stable Release
Ign:2 http://ftp.halifax.rwth-aachen.de/kali kali-rolling InRelease
Get:6 http://ftp.acc.umu.se/mirror/kali.org/kali kali-rolling Release [29.6 kB]
Get:7 http://ftp.acc.umu.se/mirror/kali.org/kali kali-rolling Release.gpg [833 B]
Get:8 http://ftp.acc.umu.se/mirror/kali.org/kali kali-rolling/main arm64 Packages [16.4 MB]
64% [8 Packages 9415 kB/16.4 MB 57%] 546 kB/s 13s
Thanking you...
Next update: 10/05/2020




Comments
Post a Comment